The loads acting on structures can be broadly classified as vertical loads, horizontal loads and longitudinal loads.
The Vertical Loads Consist Of :
1. Dead load : It is the self weight of structure which are transferred to structure throughout the life span. It majorly consists of the weight of walls, columns, beams, roofs etc.
Dead Load = volume of each section x unit weight of material
| Sl. No | Material | Unit Weight Of Material |
| 1 |
Plain Cement Concrete
|
18.8 kN/m3
|
| 2 |
Reinforced Cement Concrete
|
24 kN/m3
|
| 3 |
Brick Masonry
|
18.8 kN/m3
|
| 4 |
Timber
|
5-8 kN/m3
|
| 5 | Stone Masonry | 20.4-26.5 kN/m3 |
2. Live load : Live loads are either movable or moving load on building. It includes weights of movable partitions or furniture etc. The minimum value of live loads to be assumed are specified by the IS 875 (part 2)–1987.
Live Load For The Following Occupancies :
- Educational buildings
- Assembly building
- Institutional buildings
- Mercantile buildings
- Industrial buildings
- Business and office buildings
- Storage rooms
- Residential buildings–dwelling houses, hotels, hostels, boiler rooms and plant rooms, garages.
Imposed Or Live Load for different Occupancies :
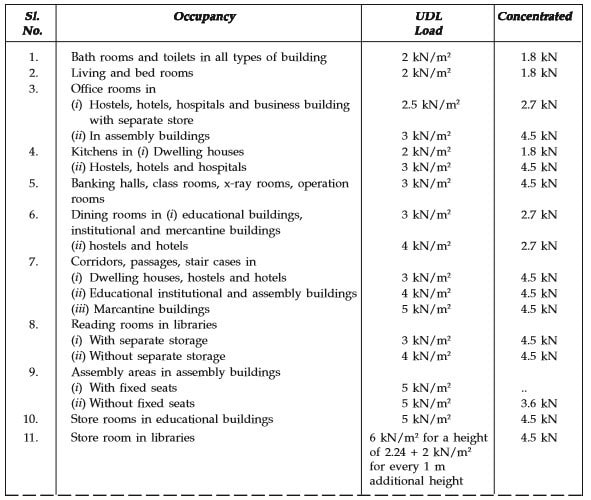 |
| IMPOSED OR LIVE LOAD ON STRUCTURE |
However, reductions in assumed total live loads on floors may be made in designing columns, walls, their supports and foundations as shown in table below.
Number of floors carried by member under consideration
|
Reduction of total live load on all floors above the member under consideration
%
|
1
|
0
|
2
|
10
|
3
|
20
|
4
|
30
|
5-10
|
40
|
Over 10
|
50
|
3. Snow load : Load caused by the snowfall on the roof of the building. It is consider as vertical load acting on a building.
According to the IS 875 (part 4) – 1987, the minimum snow load on a roof area is obtained by the expression
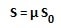
Where
S = Design snow load on plan area of roof.
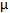
S0 = Ground snow load.
The Horizontal Loads Consist Of :
1. Wind load : It is the horizontal load caused by the blowing wind. Wind load is required to be considered in structural design especially when the height of the building exceeds two times the dimensions latreal to the exposed wind surface.
The calculation of wind loads depends on the two factors :
- Velocity Of Wind
- Size Of The Building
According to the IS-875 (Part 3) -1987) wind load calculating by the following expression :
Vz = k1.k2.k3.Vb
Where k1 = Risk coefficient
k3 = Topography factor
k2 = Coefficient based on terrain, height and structure size.
Vb = basic wind pressure is shown in a map of India.
The design wind pressure is given by :
k3 = Topography factor
k2 = Coefficient based on terrain, height and structure size.
Vb = basic wind pressure is shown in a map of India.
The design wind pressure is given by :
pz = 0.6 V2z
where
pz is in N/m2 at height Z
Vz is in m/sec.
Note : wind pressure act uniformly up to the height of 30 meter, Above 30 m height, the wind pressure increases.
2. Earthquake load : It is the vibrational load on structure caused by the earthquake. This vibration occur in all three direction, but the movement in vertical direction do not cause forces in superstructure to any significant extent. But the horizontal movement of the building at the time of earthquake is to be considered while designing.
For monolithic reinforced concrete structures located in the seismic zone 2, and 3 without more than 5 stories high and importance factor less than 1, the seismic forces are not critical.
ASCE 7-10 Wind Load Calculation Pretty good post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wanted to say that I have really enjoyed reading your blog posts. Any way I'll be subscribing to your feed and I hope you post again soon. Big thanks for the useful info.
ReplyDelete